First Aid
First aid Treatment
BURNS & SCALDS
Most people experience burns or scalds at some point in their life. Burns are caused by heat, chemicals or radiation; and scalds are caused due to hot liquids or steam. If a burn or scald occurs, first aid treatment should be applied to the affected area as quickly as possible. The goal is to relieve the pain and prevent further damage. The first aid treatment depends upon the severity or degree of burns.
- For first degree burns (the first layer of skin is damaged), keep the burned area under running cold water for at least ten minutes.
- Remove any jewelry, or watches or clothing close to the affected area.
- Cover the burn area with a sterile gauge dressing
- In case of second degree burns where blisters are formed, pour plenty of cold water over the affected area.
- Do not burst the blister, as it may lead to infection.
- Cover the unbroken affected skin area with sterile bandages to provide comfort and relief, and prevent further damage.
- Third degree burns cause damage to the nerves in the affected area, therefore the person experiences less pain. Do not use cold water or any medication over the affected area.
- Place strips of dry cloth over the damaged area, and take the victim immediately to hospital.
BLEEDING-
A person with external bleeding may experience symptoms like blood, pain at the site of injury, anxiety, light-headedness and dizziness. These symptoms depend upon the severity of bleeding, or how much the blood is lost. If a person loses too much blood, he or she may go in to shock. Hence, the first step in first aid treatment of bleeding is to stop the blood loss.
- First of all, apply pressure over the injured area using a clean cloth and your hand. Pressure basically squeezes the arteries and veins, thereby slowing the blood loss.
- Elevate the injured part or bleeding area above the person’s heart. This ensures less blood loss as blood flow has to fight the gravity.
- Put a sterile gauge or bandage over the injured part to control the bleeding. Make sure the bandage is not applied very tight as it may affect the blood circulation. If the bleeding continues, apply another gauge on it.
- Do not use tourniquet unless it has been decided to sacrifice the injured limb to save life.
- Keep on talking to the injured person to check his level of consciousness.
- In case of excessive blood loss, the person may go into shock. Hence, it is advisable to call the emergency medical help, or rush to the nearby hospital.

DROWNING-
Drowning occurs when a person is submerged in water, making it difficult for him/her to breathe. It can be fatal thing as drowning can also lead to death. The signs of drowning includes pale, cool skin, cyanosis (bluish discoloration of the skin) absence of breathing, blue lips, weak pulse or unconsciousness.
- The first step is to remove the victim from the water. Make sure to watch out for your own safety as well, as well as, do not attempt to rescue beyond your abilities.
- Call medical emergency system immediately.
- Check for vital signs, such as breathing, circulation, movement in response to stimulation.
- If the person is breathing, change his wet clothing and keep him warm.
- In case if you notice any injuries, try first aid treatment for injuries.
- If the person stops breathing, start CPR (cardiopulmonary resuscitation) immediately. Start mouth-to-mouth ventilation.
- If the victim starts coughing or spurting water from his mouth, turn him on his either side. This will help in removing water from the lungs.
- Spinal injuries are common in cases of drowning. If you suspect any spinal injury, do not try to move the patient.
- The victim is kept in hospital under observation for 24 hours.

FRACTURE-
A fracture occurs when a strong force is applied to the bones. It can be caused due to injury caused by fall or accident, or osteoporosis. Fracture or broken bone is classified in to simple and compound fracture. A simple fracture may not be visible to your through the skin. In a compound fracture, the bone protrudes out the skin. Fracture is characterized by pain at the site of injury, difficulty in moving the injured part, deformity, swelling and tenderness of the affected part and discoloration and bruising of the injured part.
- The first step is to avoid moving the affected part, unless you need to do so to prevent further injury. Let the victim lie flat on the ground. Do not move or straighten the injured bone.
- Examine the body for any bleeding, and give first aid if you notice any blood loss.
- If the victim is unconscious, administer cardiopulmonary resuscitation.
- Try to stabilize the fractured joint by applying splint. Splint helps in preventing the movement of the fractured part. This can be done with the help of padded wood or sticks. Use a handkerchief or cloth piece to tie the splint to the fractured part.
- You can also apply broad bandages to immobilize the joint. Make sure that the bandages are not too tight or loose.
- Ensure that the medical emergency services have been called.
SHOCK-
Shock is described as the condition in which the circulatory system fails and the body tissues receive insufficient supply of oxygen. It is a life-threatening condition, which if not treated on time, may lead to failure of vital organs, ultimately causing death. Shock is categorized in to three stages. Stage I is characterized by a rapid pulse and fast heartbeat. During this stage, the body tries compensatory measures to cope with the condition.
In stage II, the compensatory measures fail and the victim starts showing symptoms of weakness, giddiness, rapid shallow breathing and a weak thread pulse. The long period of circulatory insufficiency can lead to stage III, which causes permanent damage to the vital organs. The cells begin to die, and so does the victim.
- The first aid treatment for shock includes identifying the stage of circulatory shock. Let the person lie down on the floor.
- Raise the patient’s legs above the level of the heart to ensure proper blood flow to vital organs.
- Loosen the clothing, belt or any straps so as to reduce constriction around the chest.
- Try to identify the underlying cause of the shock, and treat it. For example, it could be bleeding from an external injury, removing the allergen etc. Check for signs of breathing, and give cardiopulmonary resuscitation if the victim is not breathing.
- Try to keep the patient warm and comfortable as being cold will slow down the flow of blood. But do not move the patient much around. There is no need to place a pillow under the head as this may affect breathing.
- Monitor breathing, pulse and any skin changes.
STROKE-
A stroke can be defined as the condition in which the brain cells do not receive sufficient oxygen. Due to the lack of blood supply, the brain ceases to function and brain cells begin to die. This could be due to the presence of blood clots or haemorrhage. Lack of oxygen to the brain causes symptoms such as lack of balance and stability, slurred speech, numbness or weakness on one side of the body and blurred vision. The signs of Stroke are characterized in one term- FAST- F stands for drooping of face on one side, A stands for weakness of arms or one side of the body, S stands for slurred speech and T stands for time (if you notice any other symptoms, call medical emergency immediately).
- The first and foremost step in providing first aid treatment to a stroke victim is to notice the stroke signs and symptoms and call for immediate medical help. The medical personnel on phone will guide you to take necessary steps till they reach.
- Let the victim lie down on the floor with head slightly elevated.
- Do not shake or move the victim if he or she is unconscious. Any sudden movement can cause brain damage or internal bleeding.
- If the victim is conscious, assure him that the medical assistance is on the way.
POISONING-
Poisoning occurs when any external substance interferes with the normal functioning of the body. It can occur the body by any means- by being eaten or drunk, by inhaling, by absorption through skin, or through mucus membranes of the mouth, nose and eyes.
- The appropriate first aid treatment depends upon the kind of poison the victim has consumed. While taking care of the victim with poisoning, make sure you do not become a patient yourself.
- Call medical emergency services immediately, and while they are on their way, take the below mentioned steps.
- If the victim has inhaled poison, get to fresh air immediately. Loosen tight clothing to prevent constriction.
- If the victim got poisoning via skin, remove the clothing and cleanse the affected part with running water for 15 to 20 minutes.
- In case of ingested poison, wash corrosive substance off the mouth or face. Do not try to induce vomiting. Do not give an unconscious person anything by mouth.
- After rescuing the person from danger, monitor the signs of breathing, pulse and airways. If required, start CPR.
- Do not try to neutralize the poison by antidote unless you are told by the Poison Control Center or Doctor.
ELECTRICITY-
Electricity shock usually occurs when the person has been exposed to a high voltage current or a source of electricity. This may cause injury ranging from a burn to devastating damage or death. Low voltage shock does not cause severe symptoms, whereas high voltage shocks cause severe burns and require immediate medical attention.
- Do not touch the victim if he is still in contact with the source of electricity. Your first step is to cut down the source of electricity.
- Move the body with the help of some insulating material.
- In case of minor electrical burns, give the first aid treatment for burns.
- The person may be in shock or unconscious. If the victim is unconscious but breathing, put him in the recovery position.
- Do not touch the burned or charred parts as this may further worsen the injury.
HEART ATTACK-
Heart attack is a potentially life threatening condition and it requires immediate medical attention. Many people believe that heart attack can happen only during stressful conditions or during strenuous activity. However, heart attack can happen anytime, anywhere and it could happen even while you are relaxing on a couch.
If someone around you suffers from a heart attack, the first thing you should do is to call the medical emergency number in your country to call for help. Till the time medical aid arrives, you can take a few steps to provide the first aid to the patient:
- Make the person sit or lie down while waiting for the ambulance to arrive. If the person is wearing tight clothing, it is better to loosen it up.
- If you have immediate access to aspirin or nitroglycerin, then you should administer these to the person. Aspirin will help in thinning the blood, which will prevent blood clots. Nitroglycerin helps in easing out the chest pain by opening the blood vessels, which ensures less pressure on the heart.
- Make the person feel relaxed and tell him/her that help is on the way and he/she should not be anxious. Anxiety can worsen the condition and the patient should be comforted that everything is under control and the help is on the way.
- If the condition of the person is serious and he/she has stopped breathing, then use CPR (cardio pulmonary resuscitation) to revive the patient. If you know CPR, then begin chest compression at 100 compressions per minute. After 30 compressions, begin rescue breathing.
EPILEPSY-
Epilepsy is a neurological condition in which a person may suffer from recurring seizures. A seizure is not usually dangerous or life threatening, however if the person is in a dangerous environment or is having impaired awareness during seizure or is unconscious, then it can turn out to be a risky condition. For example, seizures during driving or swimming could be risky. Good seizure control is the primary step in reducing the risks associated with epilepsy.
If you see someone suffering from seizure for the first time, it can be a frightening experience. However, if you stay calm and know the first aid response, then you can help the person having epilepsy attack. You can take the following steps on seeing a person suffering from epilepsy attack:
- Stay calm and stay with the person. Call the medical emergency number immediately.
- Try to time the duration of the seizure
- Do not try to retrain the person or hold him/her down. This may result in an injury
- You should not put any object in the person’s mouth as it may also cause injury
- Remove any harmful objects that are near the person having attack. This is a preferred approach as compared to the moving the person
- Place soft material or object under the head of the person. Loosen up any tight clothing around the neck
- After seizures have stopped, gently roll the person on to his/her side to maintain open airway. This will also prevent the patient from inhaling any secretions.
- Epilepsy attack may last anywhere between 5 minutes to 20 minutes. Do not leave the person till medical aid arrives.
CHOKING
Choking happens when a foreign object is stuck in the throat or windpipe of a person, blocking the air flow. Choking may happen due to a piece of food or in kids it may also happen due to swallowing of small objects. Choking cuts of the oxygen supply to the brain, which requires immediate aid.
If someone is choking, you can identify through the following signs:
- Difficulty in breathing
- Inability to talk
- Inability to cough with force
- Skin, nails and lips turning blue
- Loss of consciousness
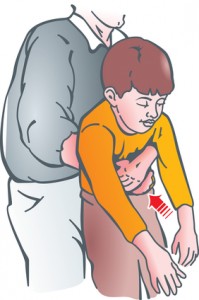
If you spot someone choking, you should immediately apply the ‘five-and-five’ approach of delivering first aid:
- Five back blows – Deliver five back blows to the person between the shoulder blades, with the use of heel of the hand
- Five abdominal thrusts – Deliver five abdominal thrusts by standing behind the person and wrapping your arms around the waist of the person. Now tip the person forward slightly. Now press hard in the abdomen of the person, giving upward thrust, as you will do if you are lifting the person up. If the person who is choked is a pregnant woman or obese, then give the thrust in to the chest, rather than abdomen.
- Alternate between 5 blows and thrusts
- If you are the only person around then you should perform the first aid before calling 911, as it is time critical to deliver the first aid to the person in such a condition.
SUNSTROKE-
Sunstroke is the most severe of the heat related problems. If proper care is not given immediately, stroke could become deadly too.
Sunstroke, also called heatstroke or hyperthermia, is caused due to body temperature rising beyond safe levels. This results in body’s core functions such as breathing, blood pumping and metabolism to stop working. If immediate attention is not provided to such a condition, it can become very dangerous. The immediate objective is to bring the body temperature of the patient below the danger limits. If you find someone around you suffering from sunstroke, here are a few steps to follow to provide the first aid to the person:
- Call for help- Call an ambulance immediately, especially if the person suffering from sunstroke has fainted. You should call nearby people for help, if you are in a public place. Ask people to bring in as much water as possible.
- Take person to a cooler place- If there is a building nearby, then take the affected person in there. Air conditioning and water will be helpful for him in this stage. If there is no building around, then you can take the person to a shade, which will be cooler than sun exposed area.
- Remove insulating clothes- If a person is wearing insulting clothes, make sure to take them off. In fact it is better to remove as much of the clothing as possible, to allow air circulation going. This will allow sweat to evaporate and will help in bringing the body temperature down.
- Apply Water Cooling- It is important not just to make the person sip some water, but you can get the water flowing on the person’s body as well. This will help in bringing the body temperature down. If the water supply is limited, then you can soak some cloth in water and pat it on person’s body, especially across the face, chest and neck. If ice cubes are available, then you can rub them over person’s body.

DEHYDRATION-
Dehydration occurs when there is shortage of water supply and imbalance in electrolytes in the body. Dehydration may be difficult to detect at times, but body does give out certain signs for us to recognize that there is severe shortage of water in the body and we need to rehydrate ourselves. Symptoms of dehydration vary according to the cause and severity of the condition. Some of the signs of mild to moderate dehydration include increased thirst, fatigue and weakness, lethargy, constipation, dry mouth, dizziness and muscle cramps.
- As soon as you feel dehydrated, stop whatever you are doing and lie down. Taking rest is the first thing to do when you feel your body is getting dehydrated.
- If you do not have any ready-made electrolyte mix at home, prepare your own rehydration drink by mixing half a teaspoon of baking soda, half a teaspoon of table salt, and two tablespoons of sugar in one glass of water.
- In case of severe symptoms of dehydration such as spastic muscles, dry wrinkled skin, parched mouth, confusion, extreme weakness, severe leg cramps, oral rehydration may not work that effectively and intravenous fluids may be required.



